
Spoofed websites are fraudulent sites that are made by cyber criminals who want to steal your money and information. They can be difficult to spot because they’re designed to imitate the look and feel of legitimate retailers. Some fake online stores will even go as far as creating their own “brand” to trick customers.

There are a lot of ways that you might come across a fake online store – like, if you’re searching for something specific and click on a link in the search results or if you click on an offer in a phishing email. The best way to protect yourself is knowing what signs to look for. Below are some common tactics that are used in spoofed websites:
Scam #1
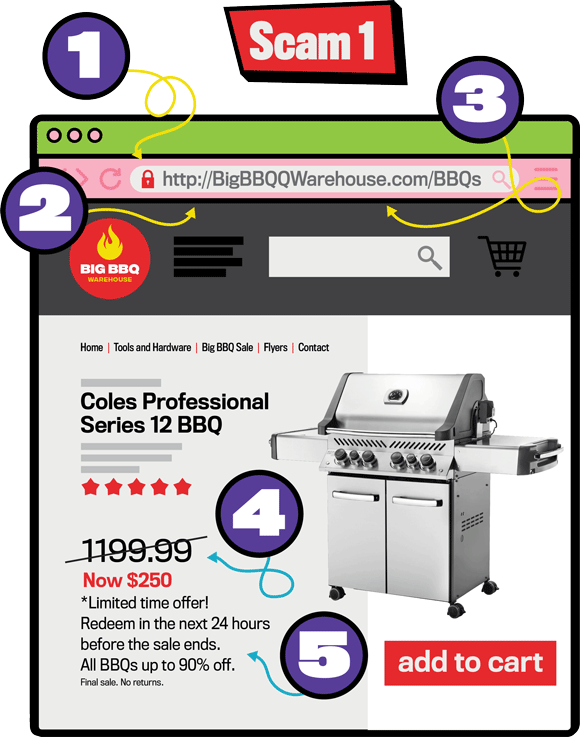
Long description - Scam 1
A fake website for an online store called Big BBQ Warehouse. Numbers surround the image to indicate the signs of phishing. One points to a lock in front of a URL. Two points to the http in the URL. Three points to the browser URL. Four points to a discounted price. Five points to text explaining a limited time offer.-

A locked padlock means a site is secure – but just because a website is secure doesn’t mean that it isn’t a scam.
-

The “s” in https stands for secure. If it’s missing, then the site isn’t secure (however, even secure sites can be scams).
-

Look for typos in the site’s address. When you’re looking for scams in real life, know that it could still be a scam even if there aren’t any typos.
-

Sales that are far too good to be true.
-

Pressures you to buy quickly.
Scam #2

Long description - Scam 2
A spoofed Amazon warehouse website. Numbers surround the image to indicate the signs of phishing. One points to an unlocked padlock infront of a URL. Two points to the browser URL. Three points to text stating 70%-90% off prices. Four points to text about using e-transfer to an email for payment. Five points to the privacy policy. Six points to the return policy.-

An unlocked padlock means that a website isn’t secure (however, even secure sites can be scams).
-

Look for typos in the site’s address or suspicious URLs using a familiar company’s name.
-

Sales that are too good to be true.
-

Legitimate companies will have secure payment systems in place and won’t ask for alternative payment methods like e-transfers. Be wary of suspicious email addresses that aren’t associated with the company in question.
-

Always look for a privacy policy and make sure that it’s legitimate.
-

Always look for a return policy and make sure that it’s legitimate.
Scam #3
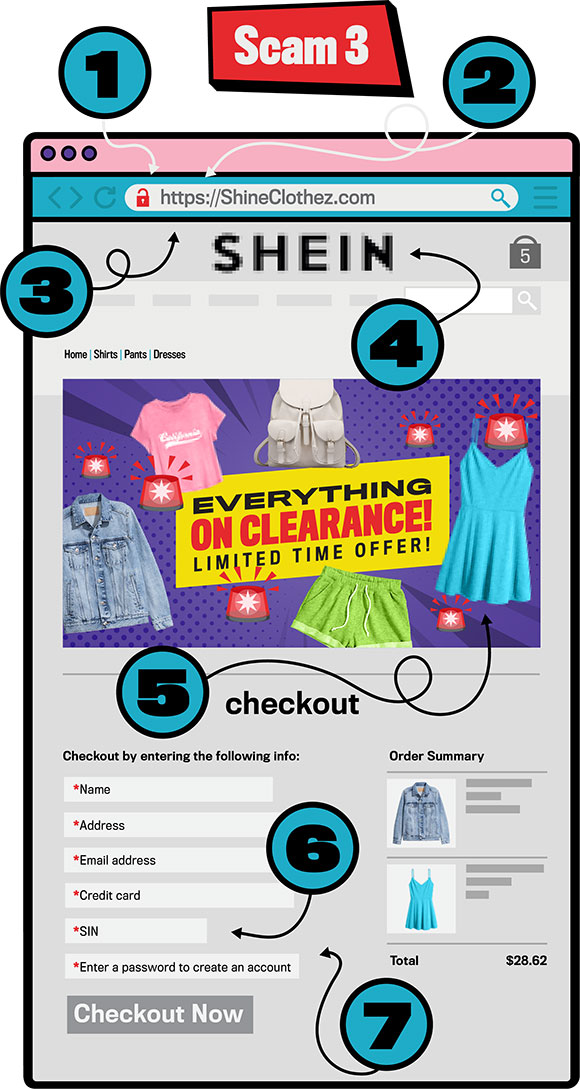
Long description - Scam 3
A spoofed Shein website. Numbers surround the image to indicate the signs of phishing. One points to an unlocked padlock infront of a URL. Two points to https in the URL. Three points to the browser URL. Four points to the blurry website title. Five points to the blurry image of advertised clothing. Six points to checkout information requesting a SIN. Seven point to the checkout information requesting a password.-

An unlocked padlock means that a website isn’t secure – however, even secure sites can be scams.
-

The “s” in https stands for secure – but just because a website is “secure” doesn’t mean that it isn’t a scam.
-

Look for typos in the site’s address. When you’re looking for scams in real life, know that it could still be a scam even if there aren’t any typos.
-

Look for blurry logos.
-

Pressures you to buy quickly.
-

Always look for a return policy and make sure that it’s legitimate.
-

Websites shouldn’t force you to make an account to checkout. But if you do, always use unique passwords online.
